The term plastics describes a group of chemicals called polymers. Heating hydrocarbons (oil, natural gas or coal) produces plastics. This process is called cracking because a catalyst is used to break larger molecules into smaller ones. The smaller molecules are those such as ethylene (ethane), C2H4; propylene (propene), C3H6; butane, C4H8; and other hydrocarbons. These chemicals, as well as styrene, are called monomers.
The Monomers are chemically bonded into chains called polymers. The properties and characteristics of these polymers vary greatly. Below are the different types of plastics with their properties and common uses.
POLYPROPYLENE (PP)
-
Translucent
-
Autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 135°C (275°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: 0°C (32°F)
Polypropylene has relatively poor impact strength, but excellent compatibility with weak and concentrated acids, bases and alcohol.* Polypropylene is commonly used to make bottles, vials, pumps, funnels and clothing.
POLYETHYLENE (PE)
-
Translucent
-
Not autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature for high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is 120°C (248°F)
-
Maximum temperature for low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is 80°C (176°F)
-
Brittleness temperature for both HDPE and LDPE is -100°C (-100°F)
Polyethylene has high impact strength and excellent compatibility with weak and concentrated acids, bases and alcohol.* Polyethylene is used to manufacture waste bags, bottles, refuse containers, pumps and secondary containment platforms.
POLYCARBONATE (PC)
-
Transparent
-
Autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 135°C (275°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: -135°C (-135°F)
Polycarbonate has high impact strength and excellent compatibility with weak acids.* Polycarbonate is commonly used to make non-breakable windows, safety eyewear and face shields.
POLYMETHYLPENTENE (PMP)
-
Transparent
-
Autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 175°C (347°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: 20°C (68°F)
Polymethylpentene has excellent compatibility with weak and concentrated acids, bases and alcohol.* Polymethylpentene is commonly used to make beakers and graduated cylinders.
PTFE Resin
-
Opaque
-
Autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 260°C (50°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: -100°C (-100°F)
PTFE resin has excellent compatibility with almost all chemicals.* PTFE resin is used to produce pumps, stoppers, tubing, containers, non-stick pans and samplers.
POLYVINYL CHLORIDE (PVC or Vinyl)
-
Clear
-
Not autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 70°C (158°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: -30°C (-22°F)
Polyvinyl chloride has excellent compatibility with almost all chemicals.* Polyvinyl chloride is used to manufacture plumbing pipes, raincoats, footwear, earplugs, pumps and tubing.
POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE COPOLYMER (PET)
-
Clear
-
Not autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 70°C (158°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: -40°C (-40°F)
Polyethylene terephthalate copolymer has excellent compatibility with weak acids, alcohol and aliphatic hydrocarbons.* It is used to make face shields and bottles.
POLYSTYRENE (PS)
-
Clear
-
Not autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 90°C (194°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: -20°C (-4°F)
Polystyrene has high strength and impact resistance and excellent compatibility with weak acids, alcohol and bases.* Ice buckets and scoops are commonly made with polystyrene.
POLYMETHYL METHACRYLATE (PMMA or Acrylic)
-
Clear
-
Autoclavable
-
Maximum temperature: 50°C (122°F)
-
Brittleness temperature: 20°C (68°F)
Polymethyl methacrylate does not have excellent compatibility with any group of chemicals.* Bench top shields and machine guards are made from polymethyl methacrylate.
*Polymers described as having excellent compatibility are generally capable of withstanding damage from the chemicals named for 30 days of constant exposure. This is only a general indication. Always check chemical compatibility with each chemical for the containers used for them.
The following plastics chart supplied by Nalgene, includes all of the plastics mentioned in this document. This chart gives many useful ratings pertaining to these plastics including temperature tolerances, permeability and sterilization processes.
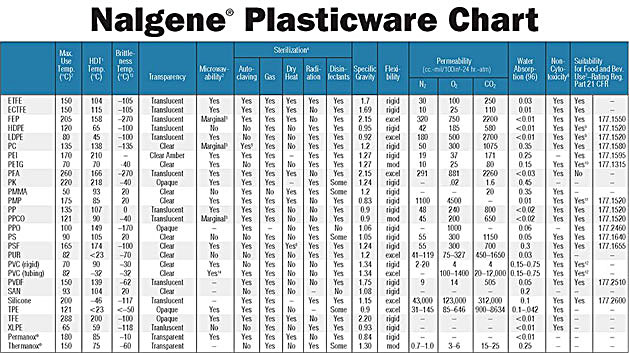
1 Heat Deflection Temperature is the temperature at which a bar deflects 0.0111 at 66 psig (ASTM D648). Materials may be used above Heat Deflection temperatures in nonstress applications; see Max. Use Temp.
2 Ratings based on five-minute tests using 600W of power on exposed, empty labware. CAUTION: Do not exceed Max. Use Temp., or expose labware to chemicals which, when heated, attach to the plastic or become rapidly absorbed.
3 Plastic will absorb heat.
4 Sterilization:
-
Autoclaving (121°C, 15 psig for 20 minutes)—Clean and rinse items with distilled water before autoclaving. (Always completely disengage threads before autoclaving.) Certain chemicals which have no appreciable effect on resins at room temperature may cause deterioration at autoclaving temperatures unless removed with distilled water beforehand.
-
Gas—Ethylene Oxide, formaldehyde, hydrogen peroxide
-
Dry Heat (160°C, 120 minutes)
-
Disinfectants—Benzalkonium chloride, formalin/formaldehyde, ethanol, etc.
-
Radiation—gamma irradiation at 25 kGy (2.5 MRad) with unstabilized plastic.
5 Sterilizing reduces mechanical strength. Do not use PC vessels for vacuum application if they have been autoclaved. Refer to Use and Care Guidelines for NALGENE Labware, for detailed information on sterilizing.
6 "Yes" indicates the resin has been determined to be noncytotoxic, based on USP and ASTM biocompatibility testing standards utilizing an MEM elution technique on a WI38 human diploid lung cell line.
7 Resins meet requirements of CFR 21 section of Food Additives Amendment of the Federal Food and Drug Act. End users are responsible for validation of compliance for specific containers used in conjunction with their particular packaging applications.
9 Acceptable for:
-
Nonacid, aqueous products; may contain salt, sugar or both (pH above 5.0)
-
Dairy products and modifications; oil-in-water emulsions, high or lowfat
-
Moist bakery products with surface containing no free fat or oil
-
Dry solids with the surfaces containing no free fat or oil (no end-test required) and under all conditions as described in Table 2 of FDA Regulation 177.1520 except condition A–high temperature sterilization (e.g. over 100°C/212°F)
10 Acceptable for:
-
Alcoholic foods containing not more than 15% (by volume) alcohol; fill and storage temperature not to exceed 49°C (120°F)
-
Nonalcoholic foods of hot fill to not exceed 82°C (180°F) and 49°C (120°F) in storage
-
Not suitable for carbonated beverages or beer, or packaging food requiring thermal processing
11 Straight-sided jars, beakers and graduated cylinders only.
12 Acceptable for aqueous, oil, dairy, acidic and alcoholic foods up to 71°C/160°F.
13 The brittleness temperature is the temperature at which an item made from the resin may break or crack if dropped. This is not the lowest use temperature if care is exercised in use and handling.
14 The tubing will become opaque from absorbed water.
NALGENE® is a registered trademark of Theremo Scientific.

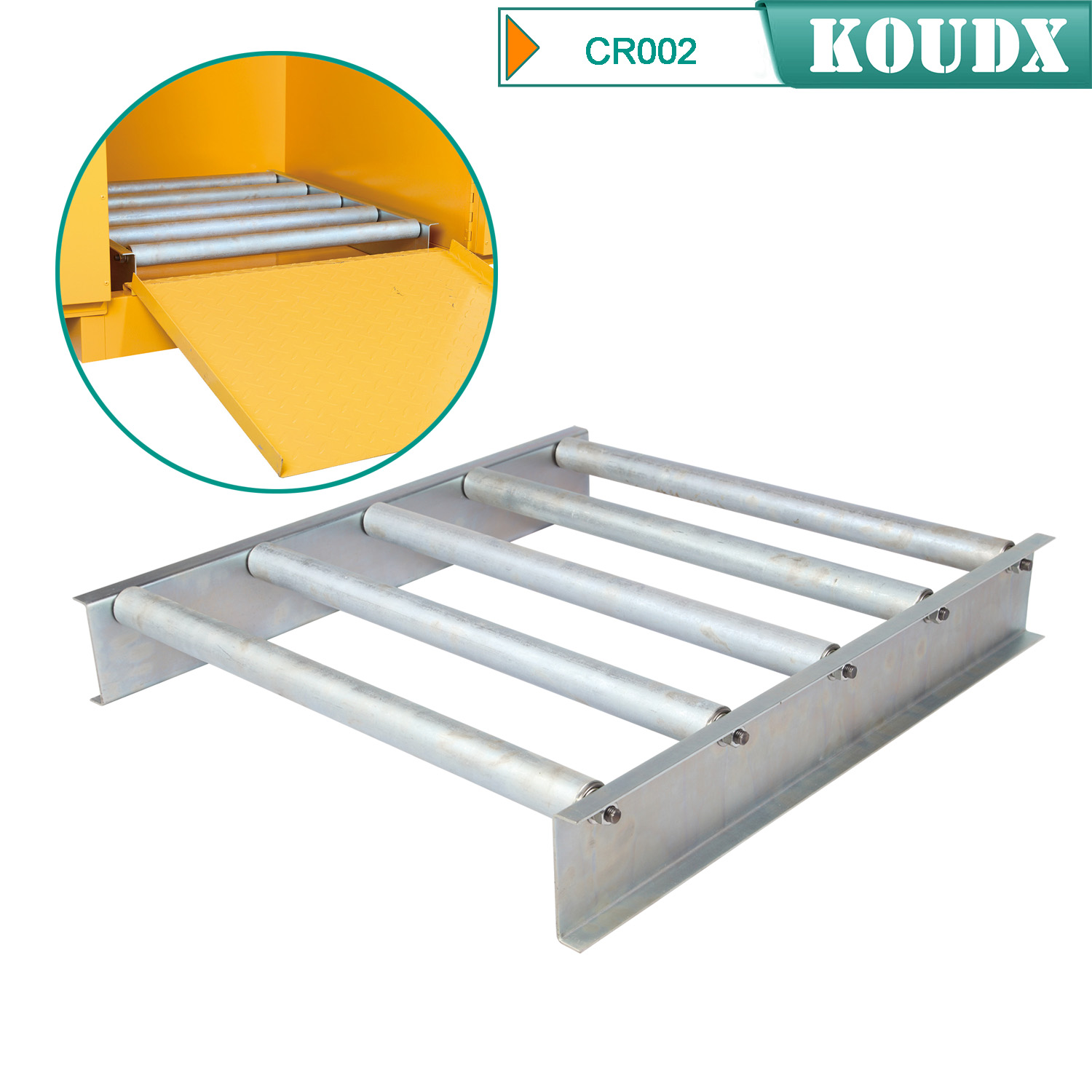
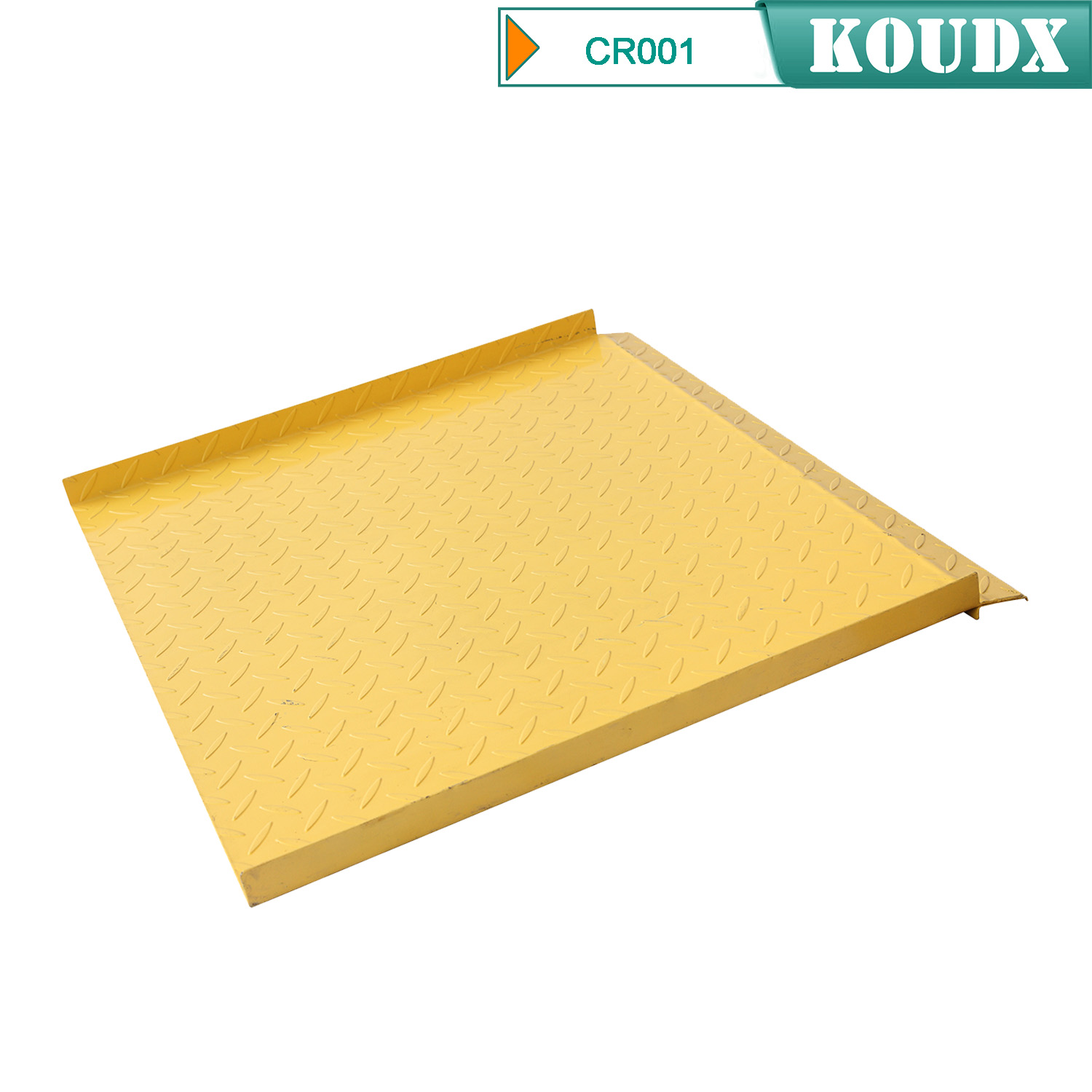
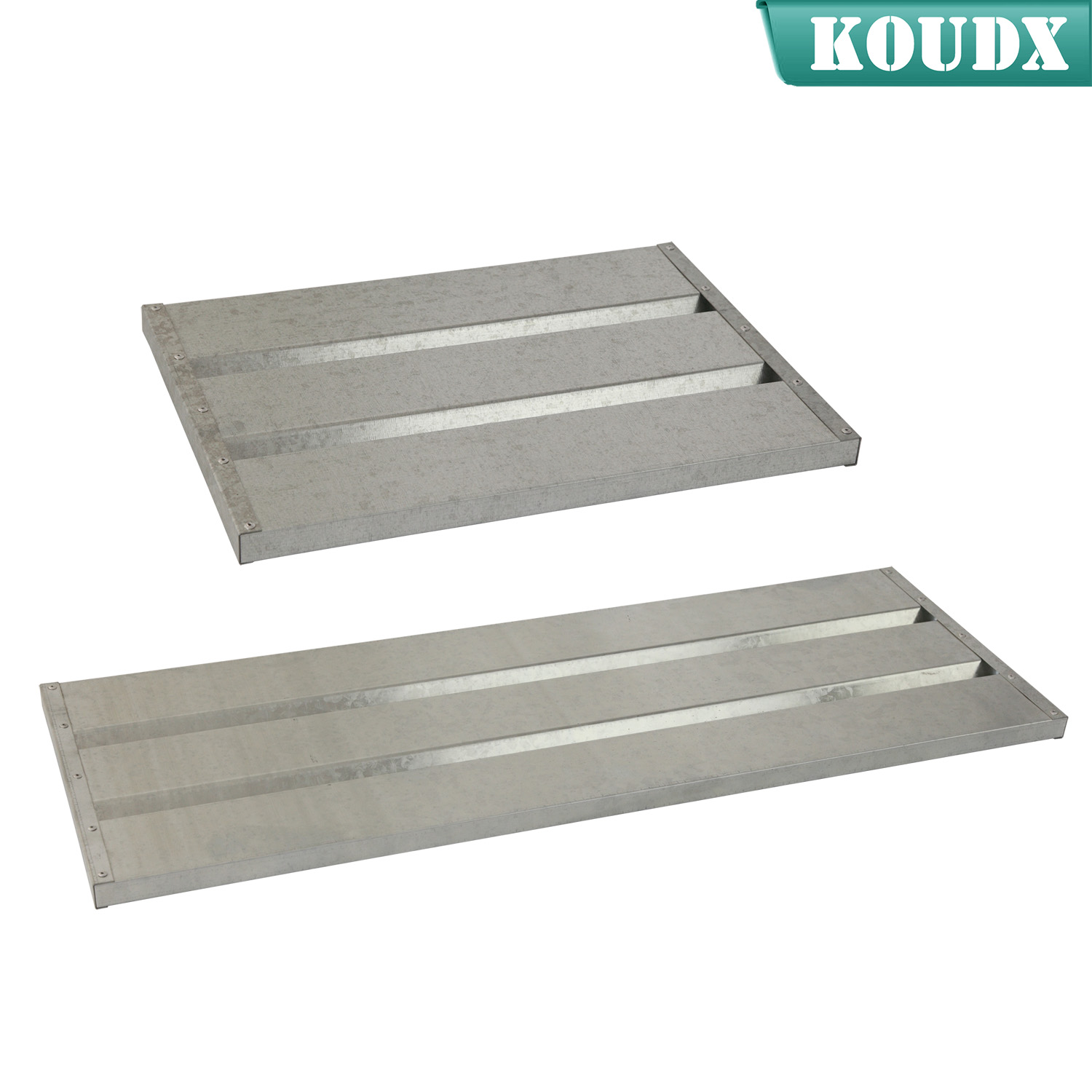
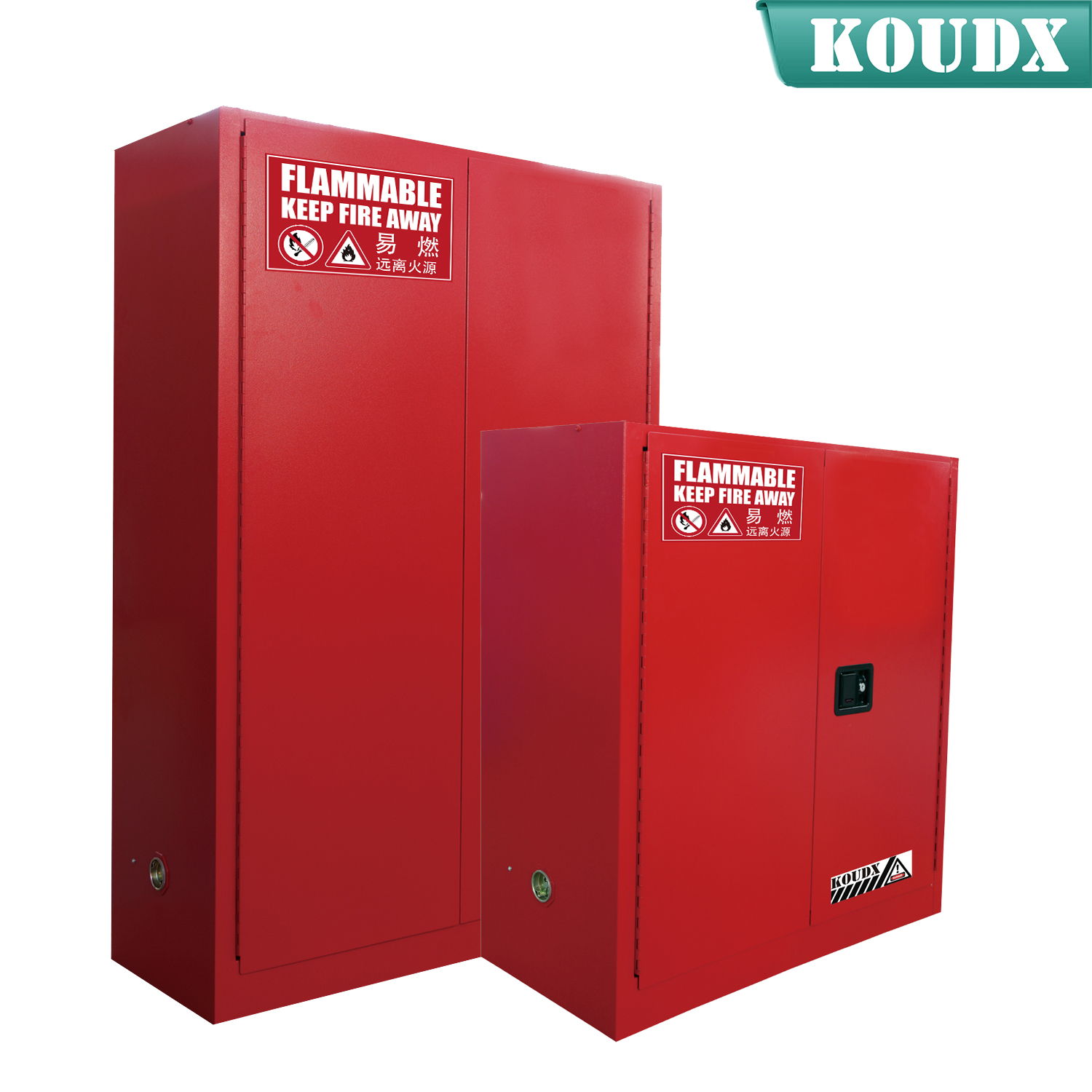
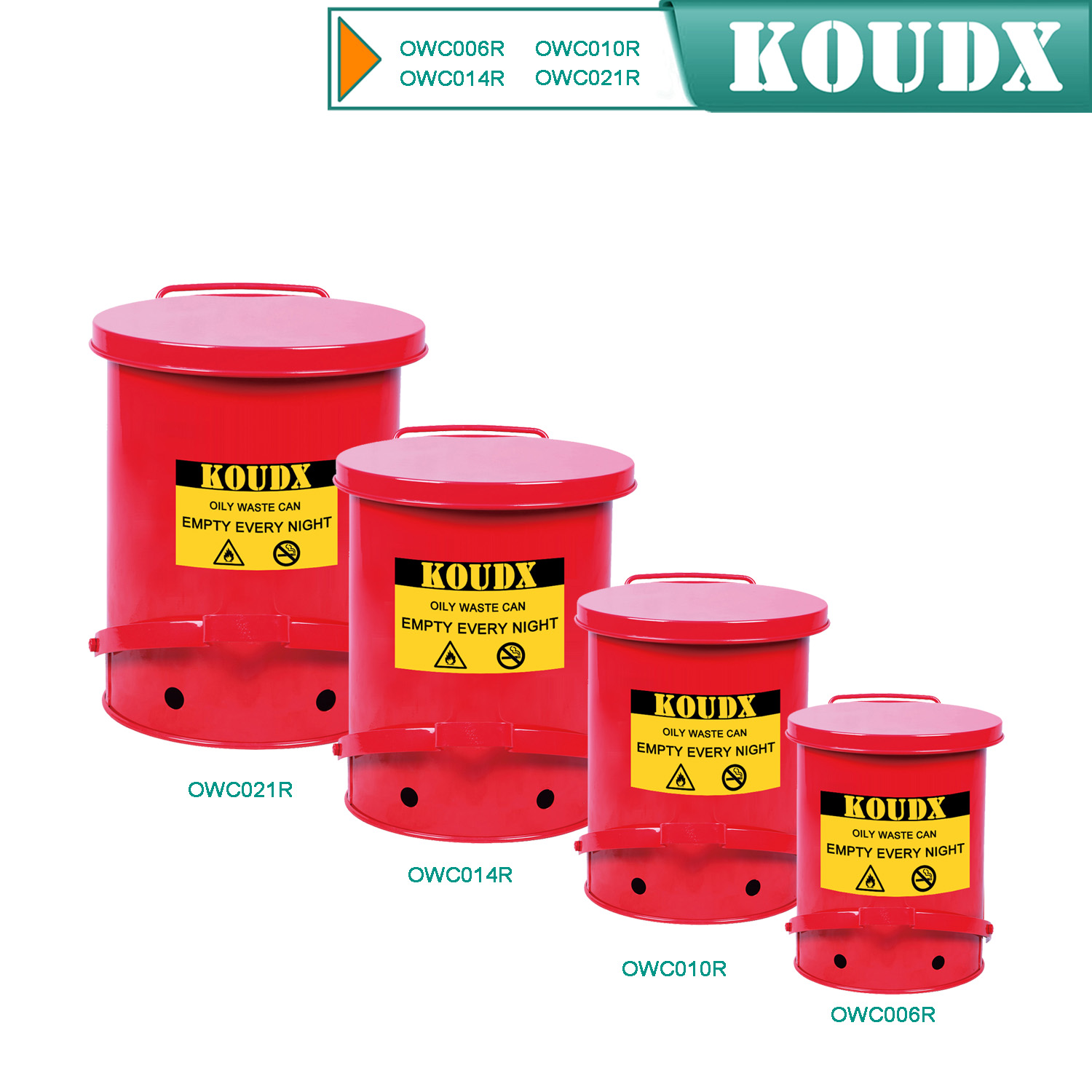
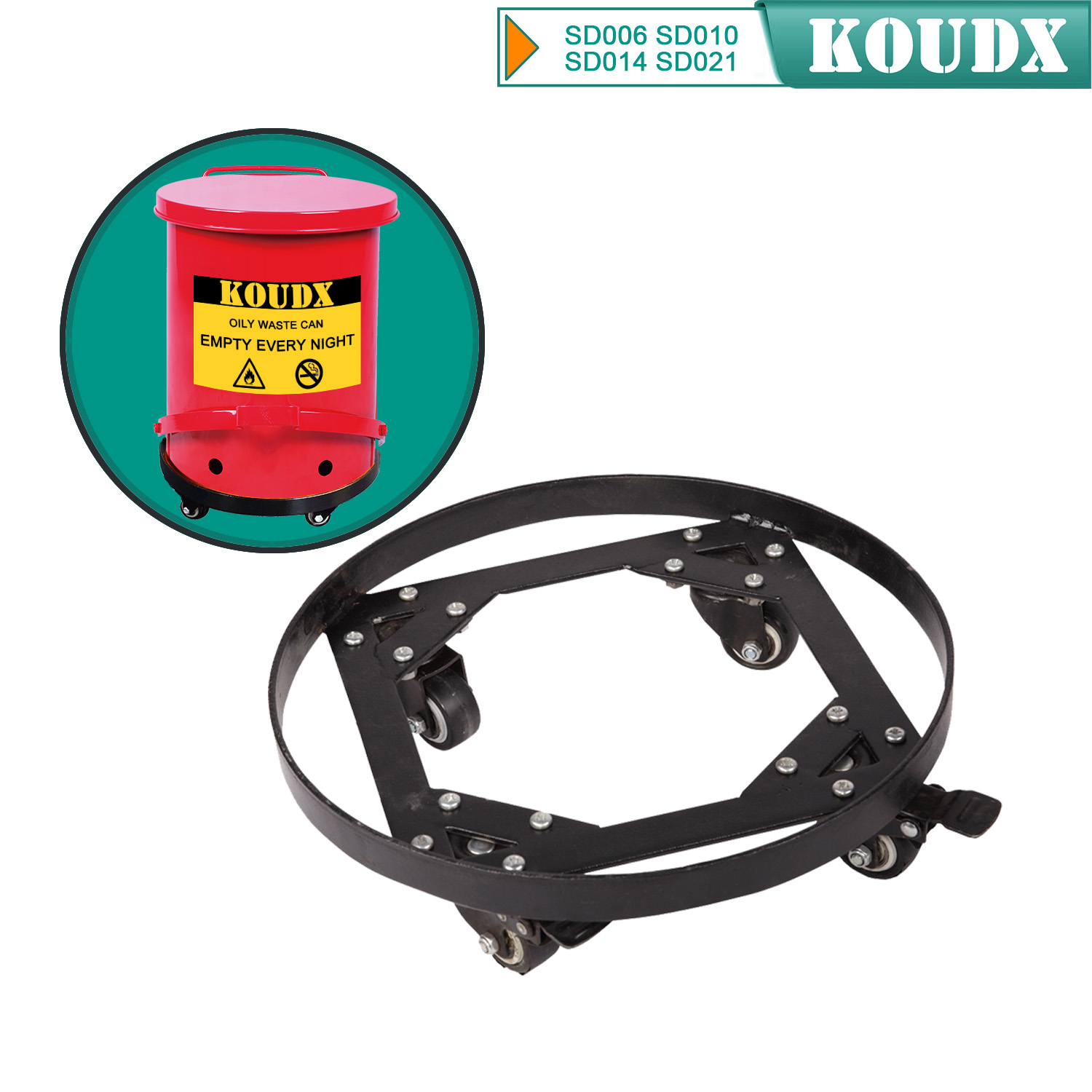
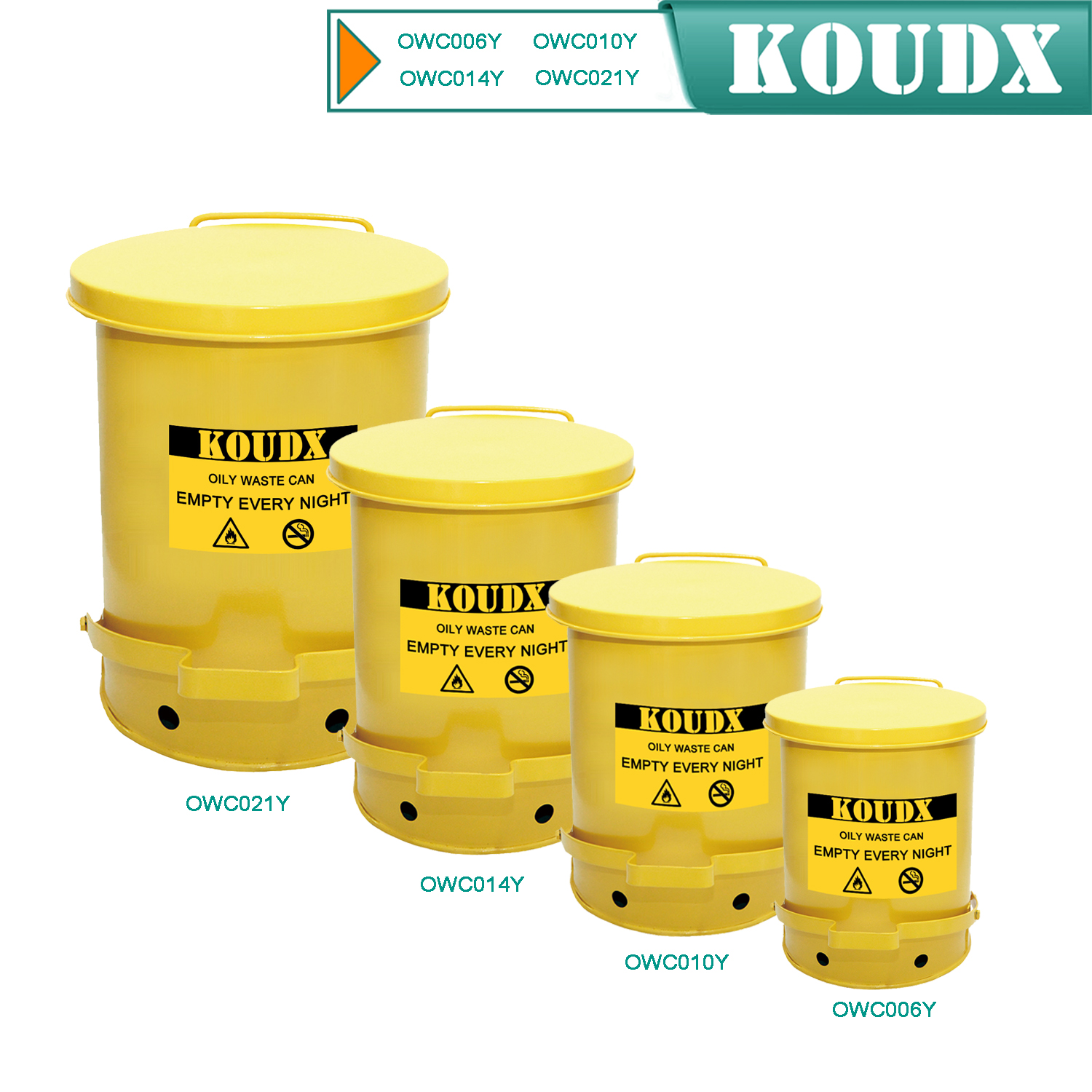
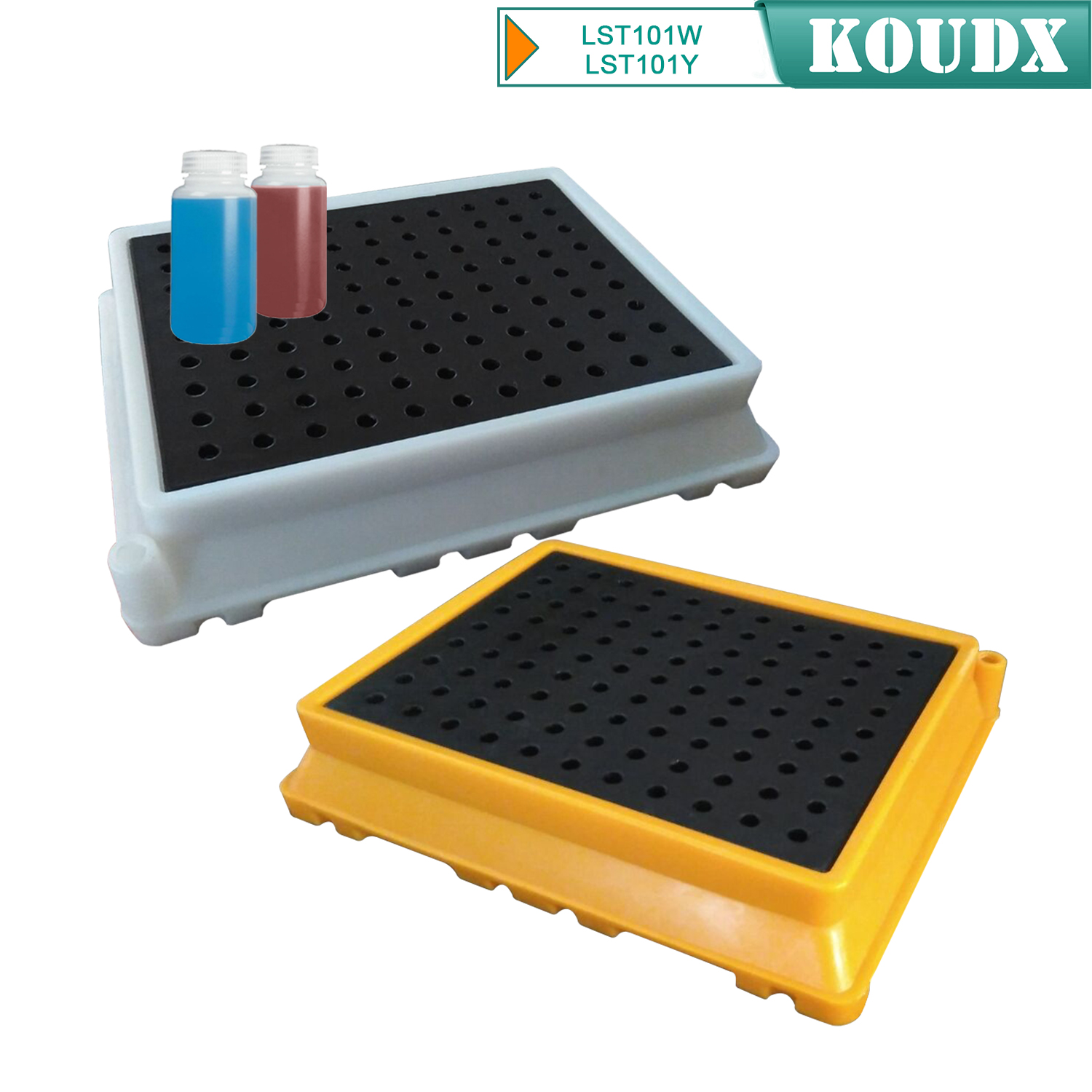
KOUDX(Shanghai Koudx Industry Technology Co., Ltd.) is a professional provider of industrial safety and environmental protection solutions. Based on the concept of market and customer demand, our fire safety cabinet was developed in accordance with the standards of OSHA 29 CER 1910.106 and NFPA CODE30. It is widely used in petrochemical industry, industrial manufacturing, university laboratories, food industry, automobile industry manufacturing, new energy and other industries.
We sincerely hope that in the journey of KOUDX's continuous development and expansion, we will be able to get the full support of our distributor partners in China and abroad, and have more long-term strategic partners, development together and achieve a win-win situation. Welcome to contact us (86) 400-168-8090, you can visit our website www.koudx.com for the detail information.




























